Abstract
Human trajectory prediction is typically posed as a zero-shot generalization problem: a predictor is learnt on a dataset of human motion in training scenes, and then deployed on unseen test scenes. While this paradigm has yielded tremendous progress, it fundamentally assumes that trends in human behavior within the deployment scene are constant over time. As such, current prediction models are unable to adapt to scene-specific transient human behaviors, such as crowds temporarily gathering to see buskers, pedestrians hurrying through the rain and avoiding puddles, or a protest breaking out. We formalize the problem of scene-specific adaptive trajectory prediction (ATP) and propose a new adaptation approach inspired by prompt tuning called latent corridors. By augmenting the input of any pre-trained human trajectory predictor with learnable image prompts, the predictor can improve in the deployment scene by inferring trends from extremely small amounts of new data (e.g., 2 humans observed for 30 seconds). With less than 0.1% additional model parameters, we see up to 23.9% ADE improvement in MOTSynth simulated data and 16.4% ADE in MOT and Wildtrack real pedestrian data. Qualitatively, we observe that latent corridors imbue predictors with an awareness of scene geometry and scene-specific human behaviors that non-adaptive predictors struggle to capture.
Results
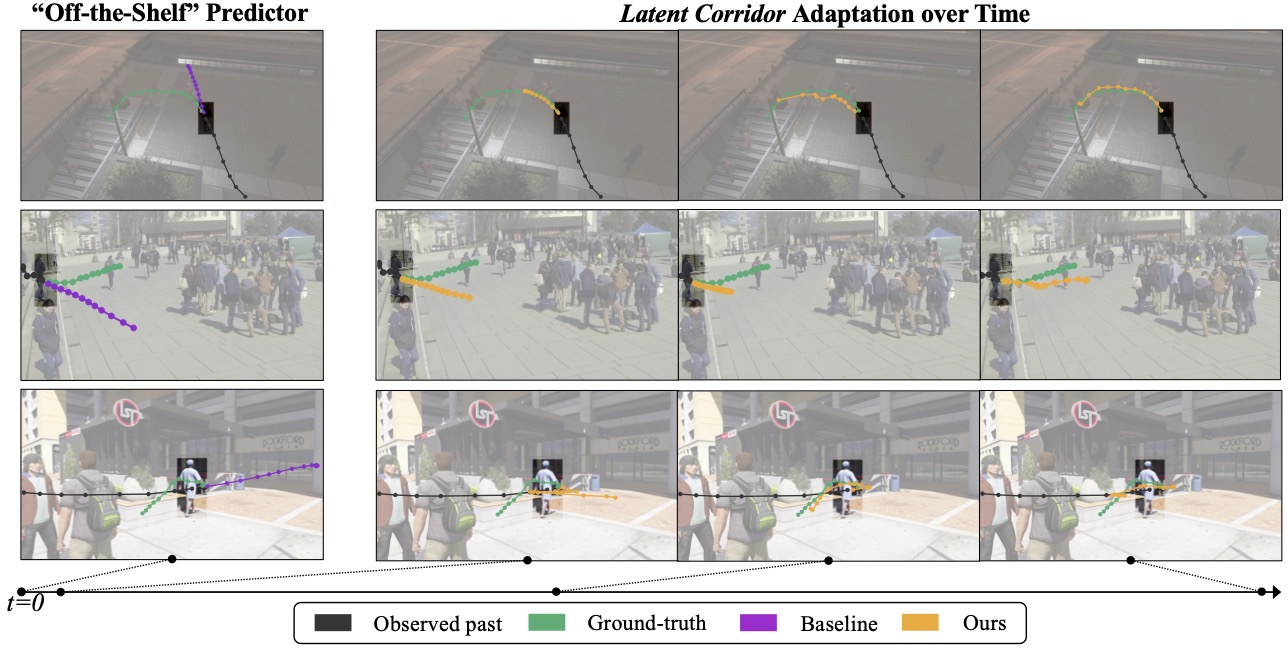
The below video shows results of our latent corridors approach to adaptive trajectory prediction on synthetic MOTSynth data and real MOT and webcam data.
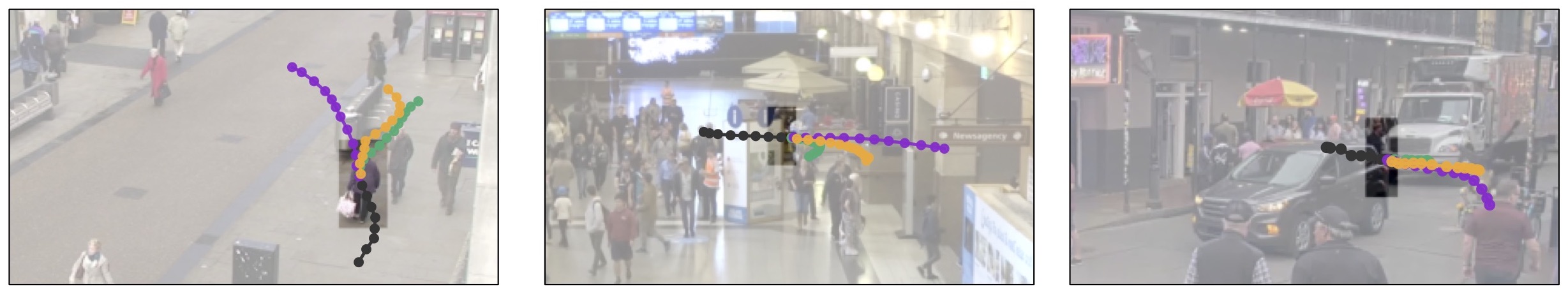
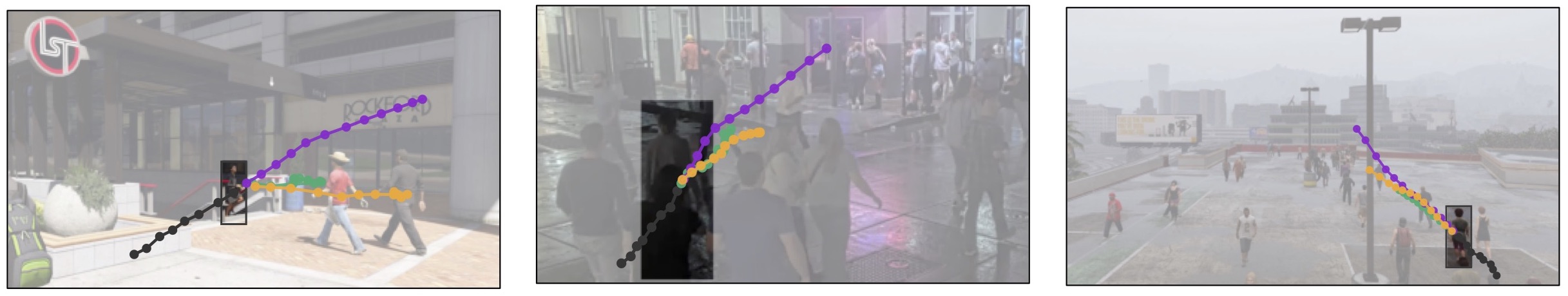
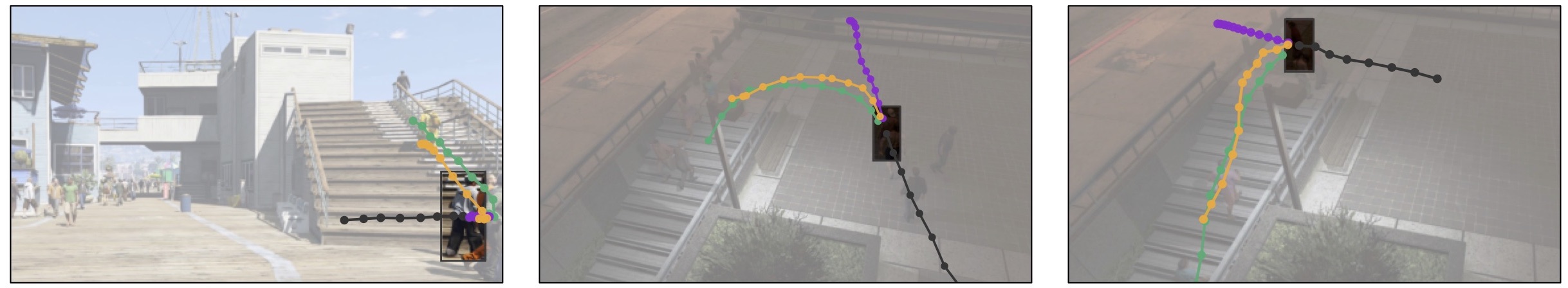
Qualitative examples of the types of awareness our latent corridors approach can imbue an adapted predictor with:




Links
Citation
@inproceedings{thakkar2024adaptive,
author = {Thakkar, Neerja and Mangalam, Karttikeya and Bajcsy, Andrea and Malik, Jitendra},
title = {Adaptive Human Trajectory Prediction via Latent Corridors},
booktitle = {European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV)},
year = {2024}
}Acknowledgments
Project webpage based on StyleGAN3.
